concurrency::accelerator
Posted
by Daniel Moth
on Daniel Moth
See other posts from Daniel Moth
or by Daniel Moth
Published on Thu, 01 Sep 2011 02:12:37 GMT
Indexed on
2011/11/11
18:19 UTC
Read the original article
Hit count: 534
GPGPU
|ParallelComputing
Overview
An accelerator represents a "target" on which C++ AMP code can execute and where data can reside. Typically (but not necessarily) an accelerator is a GPU device. Accelerators are represented in C++ AMP as objects of the accelerator class.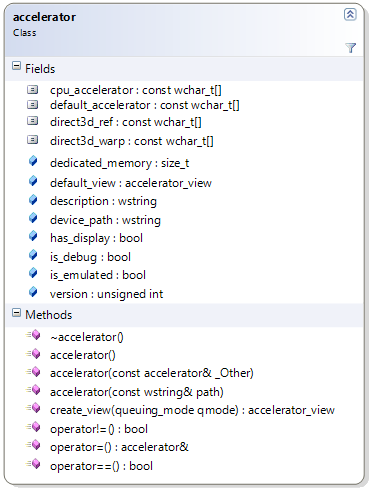
For many scenarios, you do not need to obtain an accelerator object, since the runtime has a notion of a default accelerator, which is what it thinks is the best one in the system. Examples where you need to deal with accelerator objects are if you need to pick your own accelerator (based on your specific criteria), or if you need to use more than one accelerators from your app.
Construction and operator usage
You can query and obtain a std::vector of all the accelerators on your system, which the runtime discovers on startup.
Beyond enumerating accelerators, you can also create one directly by passing to the constructor a system-wide unique path to a device if you know it (i.e. the “Device Instance Path” property for the device in Device Manager), e.g. accelerator acc(L"PCI\\VEN_1002&DEV_6898&SUBSYS_0B001002etc");
There are some predefined strings (for predefined accelerators) that you can pass to the accelerator constructor (and there are corresponding constants for those on the accelerator class itself, so you don’t have to hardcode them every time). Examples are the following:
- accelerator::default_accelerator represents the default accelerator that the C++ AMP runtime picks for you if you don’t pick one (the heuristics of how it picks one will be covered in a future post). Example:
accelerator acc; - accelerator::direct3d_ref represents the reference rasterizer emulator that simulates a direct3d device on the CPU (in a very slow manner). This emulator is available on systems with Visual Studio installed and is useful for debugging. More on debugging in general in future posts. Example:
accelerator acc(accelerator::direct3d_ref); - accelerator::direct3d_warp represents a target that I will cover in future blog posts. Example:
accelerator acc(accelerator::direct3d_warp); - accelerator::cpu_accelerator represents the CPU. In this first release the only use of this accelerator is for using the staging arrays technique that I'll cover separately. Example:
accelerator acc(accelerator::cpu_accelerator);
You can also create an accelerator by shallow copying another accelerator instance (via the corresponding constructor) or simply assigning it to another accelerator instance (via the operator overloading of =). Speaking of operator overloading, you can also compare (for equality and inequality) two accelerator objects between them to determine if they refer to the same underlying device.
Querying accelerator characteristics
Given an accelerator object, you can access its description, version, device path, size of dedicated memory in KB, whether it is some kind of emulator, whether it has a display attached, whether it supports double precision, and whether it was created with the debugging layer enabled for extensive error reporting.
Below is example code that accesses some of the properties; in your real code you'd probably be checking one or more of them in order to pick an accelerator (or check that the default one is good enough for your specific workload):
void inspect_accelerator(concurrency::accelerator acc)
{
std::wcout << "New accelerator: " << acc.description << std::endl;
std::wcout << "is_debug = " << acc.is_debug << std::endl;
std::wcout << "is_emulated = " << acc.is_emulated << std::endl;
std::wcout << "dedicated_memory = " << acc.dedicated_memory << std::endl;
std::wcout << "device_path = " << acc.device_path << std::endl;
std::wcout << "has_display = " << acc.has_display << std::endl;
std::wcout << "version = " << (acc.version >> 16) << '.' << (acc.version & 0xFFFF) << std::endl;
}
accelerator_view
In my next blog post I'll cover a related class: accelerator_view. Suffice to say here that each accelerator may have from 1..n related accelerator_view objects. You can get the accelerator_view from an accelerator via the default_view property, or create new ones by invoking the create_view method that creates an accelerator_view object for you (by also accepting a queuing_mode enum value of deferred or immediate that we'll also explore in the next blog post).
Comments about this post by Daniel Moth welcome at the original blog.
© Daniel Moth or respective owner